Reading
- MSP430 Family User Guide
- Sections 3.3 Addressing Modes
- Section 3.4 Instruction Set
- Debuggers
- MSP430 Instruction Set
Homework
Please type all homework.
Integrity: Your honor is extremely important. This academic security policy is designed to help you succeed in meeting academic requirements while practicing the honorable behavior our country rightfully demands of its military. Do not compromise your integrity by violating academic security or by taking unfair advantage of your classmates.
Note: These questions are based on both the class slides and the reading above.
Note: This is due the beginning of lesson 6.
- Not due until lesson 6, but you need to start on it before it is due:
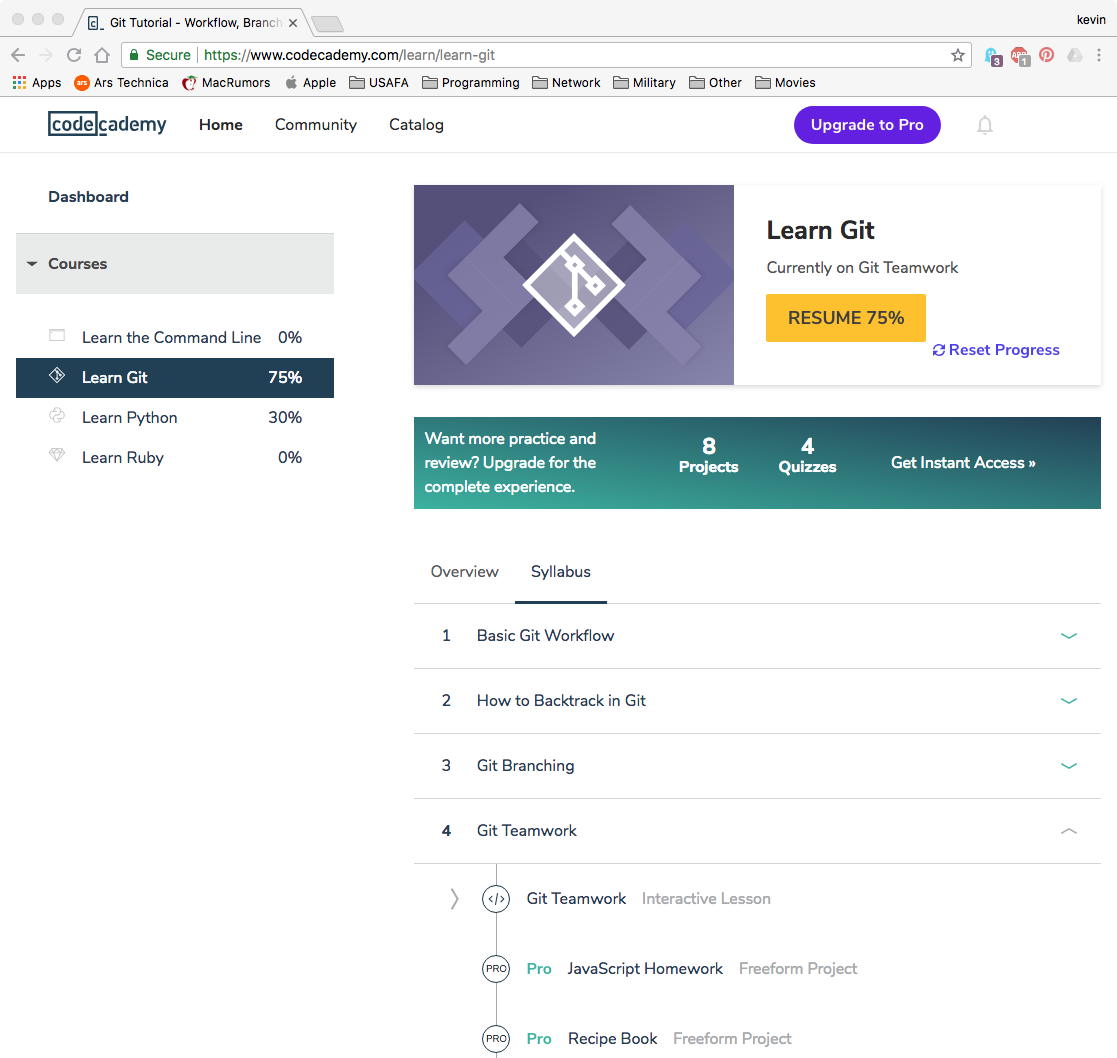
- Make an account at www.codecademy.com and take the “Learn Git” class.
- You are taking the free version, so you don’t have to pay for anything and don’t try to do anything labelled “Pro”
- There are several lessons for the “Pro” version, but you have to pay for those, don’t take them. The system should automatically skip you over them although there are several pop-ups to get you to join.
- Please pay attention to this lesson, you will be quizzed and tested on this material.
- You might want to keep some notes on what the commands do so you can review for the quiz or test
- When you are done, turn in a screenshot of your progress, it should look like this, but read 100% complete (ignore the other courses in the picture)
- For a jump instruction, how many bits is the PC offset and what is your jump range? (Hint: is the PC offset signed or unsigned?)
- What are emulated instructions and how do they differ from the 3 other instruction types?
- What is the formula for the new PC in a jump instruction?
- hint: PC_new = ____ + _____ + _____ x ______
- Identify the addressing modes for each of the following:
mov r8, r9mov @r8, r9mov @r8+, r9mov @r8, r9
- Convert the following assembly in to machine code:
mov.b #0x75, r10 - Convert the following assembly in to machine code:
mov #170, r10 - Convert the following assembly in to machine code:
mov @r7, r8 - Convert the following assembly in to machine code:
xor @r12+, 0(r6) - What does the command
clrcdo? - What is the command
jnand what status bit does it look at? - For
jncif the status bit C=0, what value gets put into PC? - For
jloif the status bit C=0, what value gets put into PC? - How are the commands
rraandrrcdifferent? - For
subc, what is the destination register equal to? - For
tst, what are the status registers set to? - If you did
tst r9, is the value of r9 changed? - How does
tstandtst.bdiffer in operation? - Which command produces larger code and why?
add #200, r10oradd r3, r4 - Is the instruction
add #200, #5000valid? Why or why not? - Which status register flags affect the following jump commands?
- JNE
- JN
- JMP